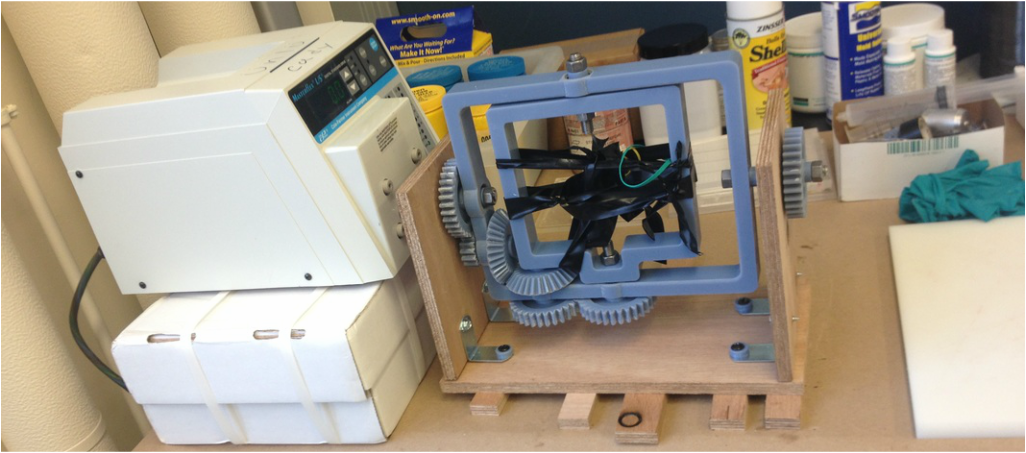
Rotational Molding Machine
Objectives of my experience at the Organics Robotics Lab were:
- Create optimal soft elastomeric actuators that will act as artificial joints that will help people with arthritis improve their arm motor functions.
- Improve the performance of soft actuators via mechanical design and by developing new rapid prototyping systems.
Related journal article :
Scalable manufacturing of high force wearable soft actuators
by Huichan Zhao, Yan Li, Ahmed Elsamadisi, Robert Shepherd
Scalable manufacturing of high force wearable soft actuators
by Huichan Zhao, Yan Li, Ahmed Elsamadisi, Robert Shepherd
Introduction
|
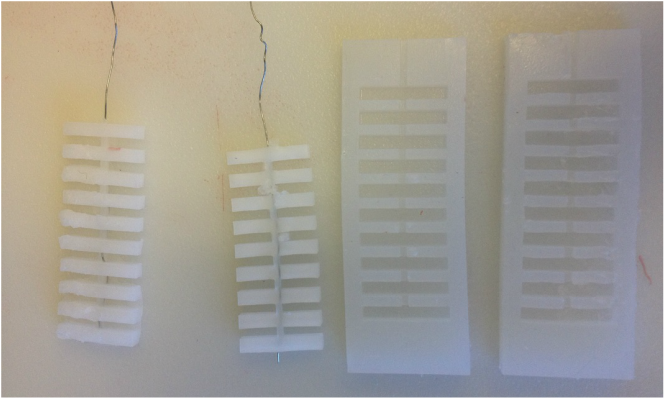
The research group of one PhD student and two undergraduate students including myself went through various silicone actuator prototypes and fabrication methods.
The group had trouble with devising a soft actuator with two layers being stretchable on one side and not stretchable on the other side. Our various attempts included designing several molds, layering silicone of varying Young's Moduslus, and employing carbon fibers in different directions. |
|
The main problem was the production method. Manually pouring down silicone to the mold would create unintentional holes as well as uneven internal surface.
One of the fabrication method was to use a fugitive ink with crystalline wax to occupy the internal space. However, the wax would
|
Brainstorming
|
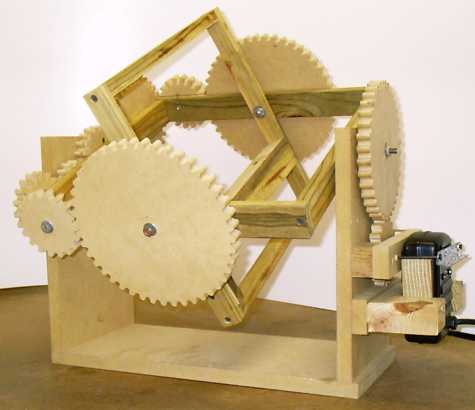
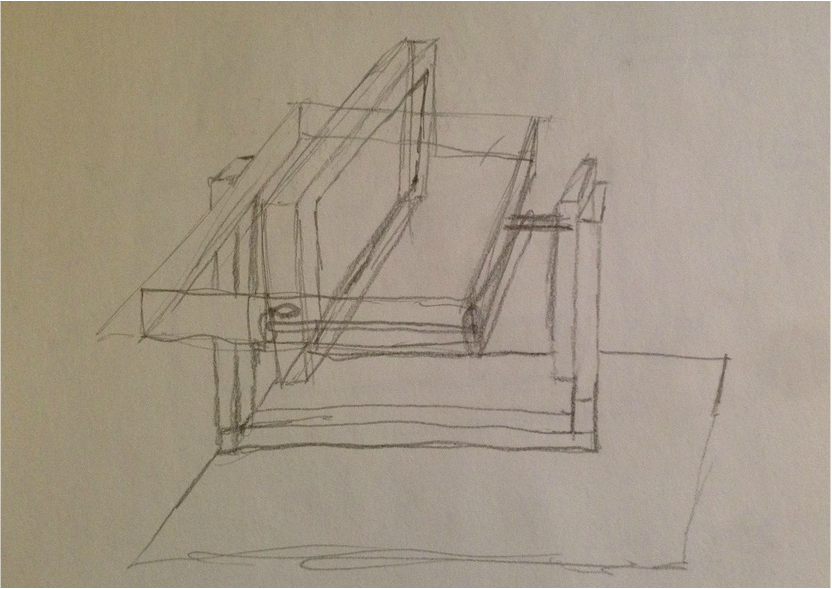
Professor Shepherd suggested the group of building the rotational molding machine. The rotational molding machine would displace the silicone material to the inner side of the actuator, and therefore, reducing the clumps in the middle of the actuator and allowing a uniform air pocket inside. I found some images of the machine online to start brainstorming of the design.
|
|
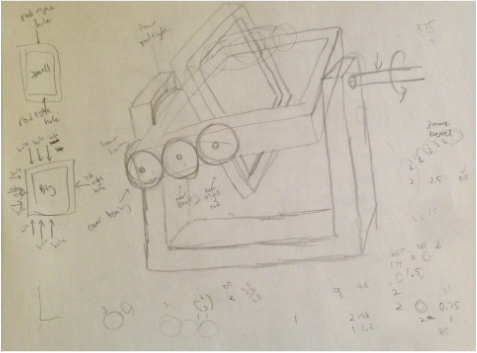
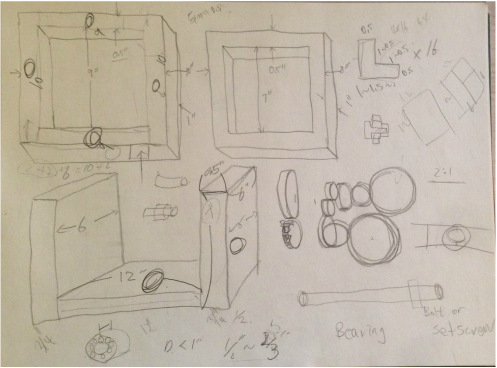
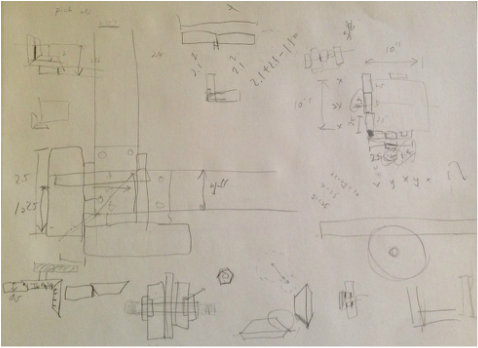
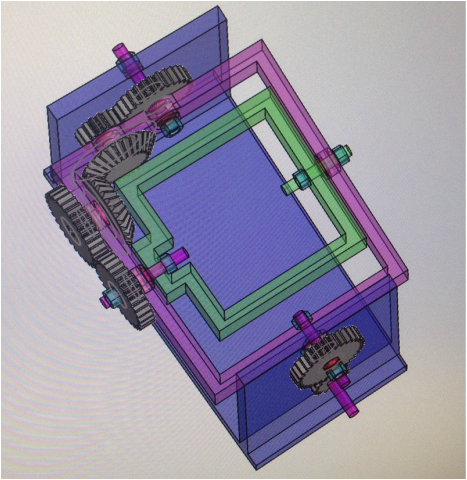
Based on the images found online, I sketched the rotational molding machine and figured out the components for designing CAD and ordering purpose.
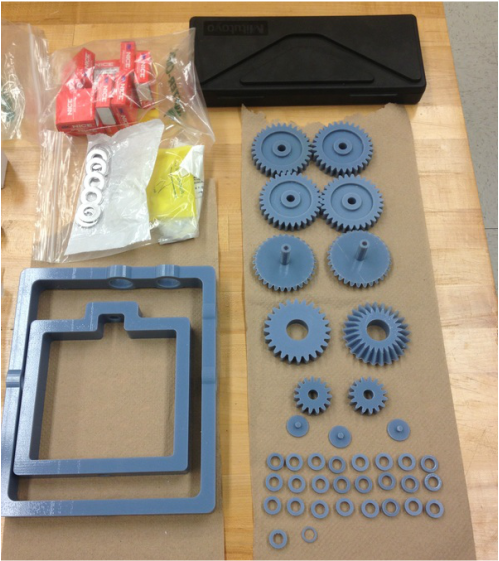
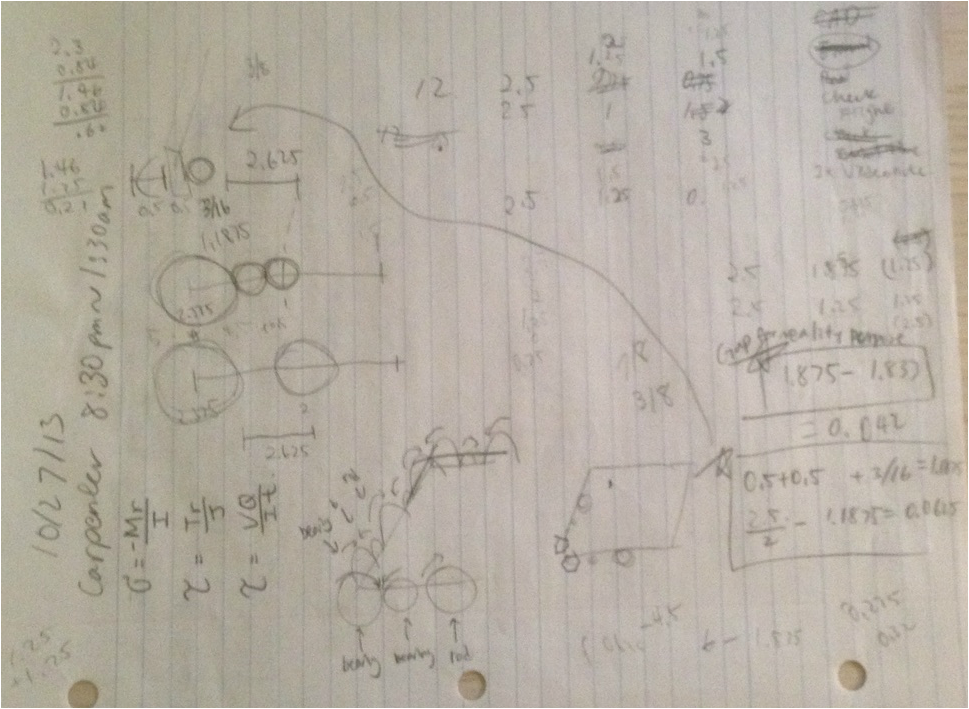
The dimensions of the components were determined during the brainstorming process. The group discussed the minimum area required for the size of the actuator mold. I also researched the gear size and ratio to minimize the total number of gears used for simplicity sake. Based on the geometry and dimensions from brainstorming, the PhD student and I made CAD for the rotational molding machine. |
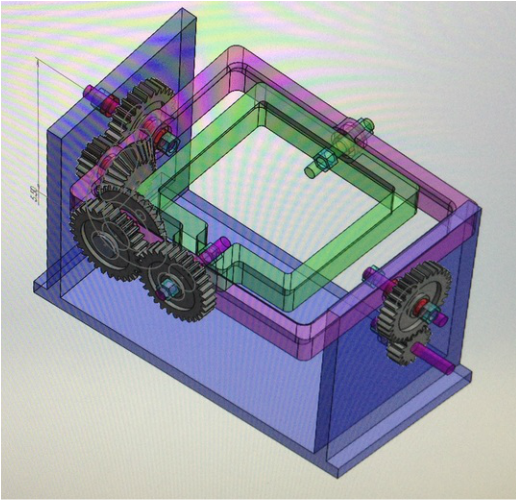
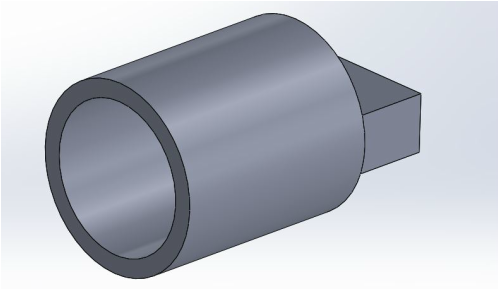
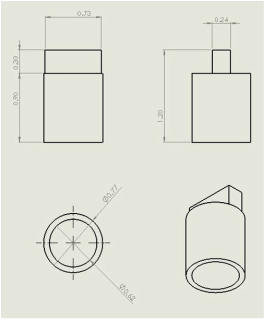
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
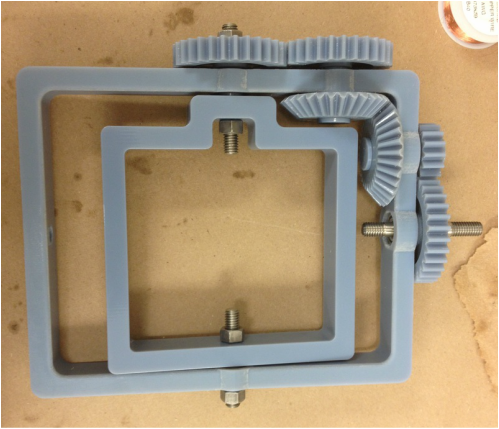
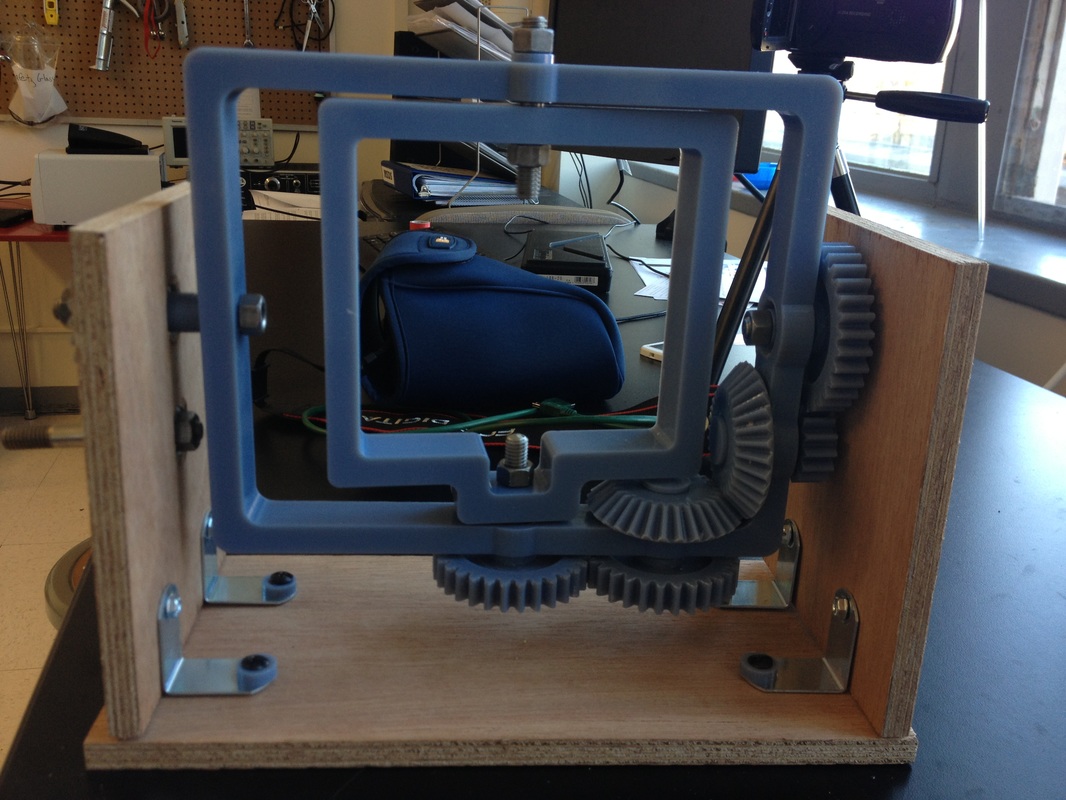
Parts 3D Printed
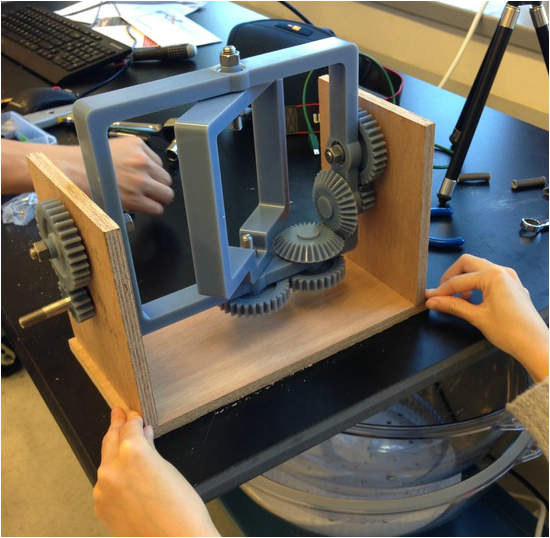
Assembly
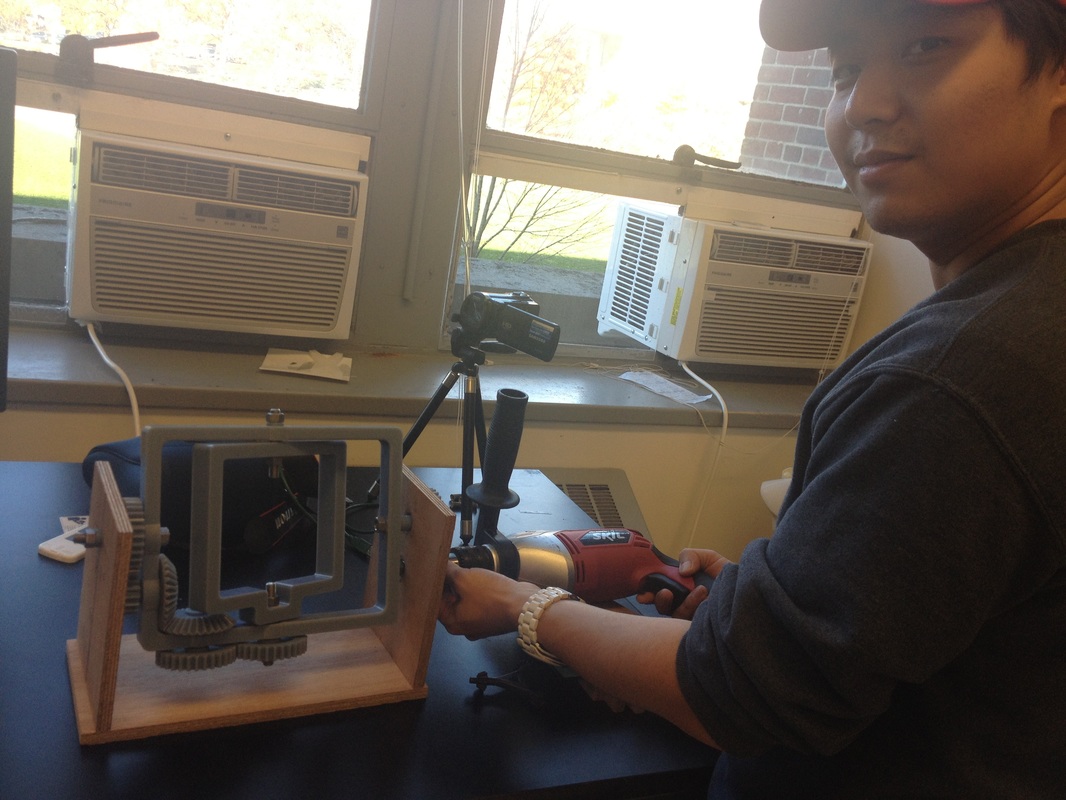
Fixture to rest the mold was not yet implemented in the picture. The group temporarily used rubber band and tapes to hold the mold. The group needed to adjust to the appropriate rotational speed for uniform wall thickness of the actuator, but the rotational molding machine was successfully built.
The rotational molding machine contributed greatly towards the improvement of the soft actuator in terms of function and design. After using this version of the machine for a while, the lab came up with an upgraded version built with metal.